How to Treat and Prevent Hyperpigmentation in Dark Skin Tone?
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that causes areas
of excess melanin, resulting in dark spots and uneven skin tone. While it can affect individuals
with various skin tones, those with darker skin tones, such as brown and black skin, frequently
face different obstacles in treatment. This blog will discuss the causes of hyperpigmentation,
the particular challenges of treating it in darker skin, and effective treatment methods.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation happens when excessive pigment is produced in particular parts of the skin. It can occur via factors including:
Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) rays stimulate melanocytes (the cells that produce melanin), leading to increased pigmentation.
Inflammation
Conditions such as acne, eczema, or other skin irritations can trigger post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH),
where areas of the skin darken after an inflammatory event.
Hormonal Changes
Conditions like melasma are often influenced by hormonal fluctuations,
commonly seen during pregnancy or with the use of hormonal contraceptives.
Genetics
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to develop hyperpigmentation.
Darker skin includes more melanin, which also provides better UV protection.
However, more melanin may highlight dark areas when hyperpigmentation occurs.
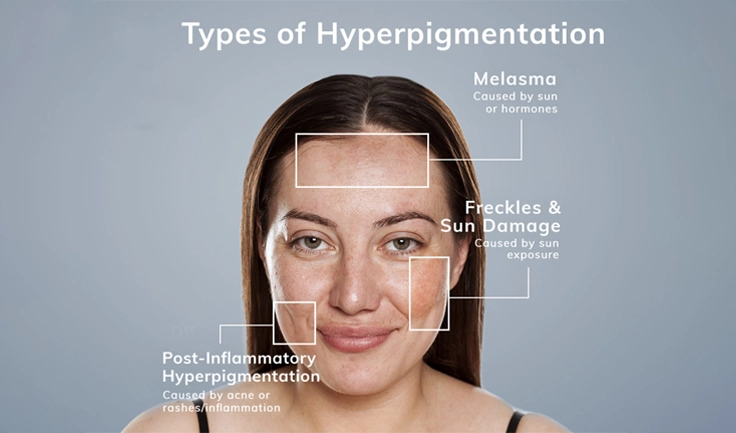
Know About Hyperpigmentation in Dark Skin
Hyperpigmentation may appear in many different forms, including sun
spots, melasma, and PIH. These disorders can cause important discolouration on darker
skin. Because darker skin tones already have a high melanin content, any disruption—whether
from sun exposure, trauma, or hormonal changes—can cause pigment overproduction, making black spots appear darker.
The Risks of Treatment
Traditional treatments like topical medications, chemical peels,
and laser therapy can sometimes cause hyperpigmentation in dark skin if not handled
correctly, primarily due to the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which
occurs when skin darkens due to irritation or trauma.
Preventative Measures
- Sun Protection One of the most crucial steps in managing hyperpigmentation is
effective sun protection. UV exposure can exacerbate existing pigmentation and
trigger new dark spots. Here are some guidelines
- Daily Sunscreen Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at
least SPF 30 every day, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, especially when outdoors.
- Protective Clothing Wear hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves to shield your skin from direct sunlight.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours Limit sun exposure during peak hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Gentle Skincare
Being gentle with your skin is vital to prevent trauma that can lead to further pigmentation:
Avoid Physical Exfoliants
Opt for chemical exfoliants instead of harsh scrubs, which can irritate the skin.
Care with Active Ingredients
Introduce active ingredients gradually. Some products can irritate, leading to PIH.

Some Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
Hydroquinone Cream for Melasma & Hyperpigmentation
Hydroquinone is a potent skin-lightening agent that inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, an important component in melanin production.
Effectiveness
Hydroquinone is a potent treatment for hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones, by reducing dark spots and improving skin tone.
Usage
Typically, hydroquinone is used in concentrations of 2% over the counter or up to
4% by prescription. It is generally recommended to use it for a limited time, followed
by a break to prevent potential side effects, such as ochronosis (a bluish-black discolouration).
Caution
Monitor for irritation or allergic reactions, and consult a dermatologist for guidance.
Kojic Acid Serum For Pigmentation & Dark Spots
Both arbutin and kojic acid are milder alternatives that also inhibit tyrosinase, but they function differently:
Arbutin for Skin Lightening
Hydroquinone derivative offers gentle skin lightening with longer results but lower irritation risk, albeit taking longer to see results.
Kojic Acid to Reduce Skin Hyperpigmentation
Kojic acid, a common ingredient in skin-lightening products, inhibits melanin production to improve skin brightness, but its effectiveness may vary based on skin type.
Azelaic Acid for Skin Whitening
Azelaic acid is another beneficial option for treating hyperpigmentation, particularly PIH:
Mechanism
It works by targeting hyperactive melanocytes without affecting normal skin cells, making it a gentler option.
Effectiveness
Azelaic acid, although slower-acting than stronger agents, is well-tolerated and less likely to irritate, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
Retinoid Treatment for Skin Problems
Retinoids, such as tretinoin, are derivatives of vitamin A that promote cell turnover and can help fade hyperpigmentation:
Benefits
They not only help in reducing dark spots but also improve skin texture and address signs of ageing.
Usage
Retinoids should be used at a low concentration and gradually increased as tolerated to prevent irritation, and often combined with other treatments for optimal results..
Effect of Vitamin C Serum on melanin pigmentation
Ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, is a powerful antioxidant that can help brighten the skin and inhibit melanin production:
Effectiveness
While less potent than hydroquinone or retinoids, vitamin C can still contribute to an overall brighter complexion and help prevent new hyperpigmentation.
Formulations
Look for stabilized formulations, as vitamin C can degrade quickly in sunlight.
Exfoliating Acids for Skin Peeling Solution
Exfoliating acids can assist in fading hyperpigmentation, but caution is essential with darker skin:
Gentler Options
Consider using mandelic acid or polyhydroxy acids (PHAs), which are milder than glycolic acid and less likely to irritate.
Gradual Introduction
Start with low concentrations and increase as your skin tolerates, monitoring for any signs of irritation.
Professional Skin Pigmentation Treatment:
Chemical Peel for Dark Spots & Hyperpigmentation
Chemical peels can effectively address hyperpigmentation by removing the outer layers of skin
Choice of Peel
For darker skin tones, lighter peels (such as lactic or mandelic acid peels) are often safer options. Avoid deep peels,
which can increase the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Consultation
Always seek an experienced practitioner who understands how to treat darker skin tones safely.
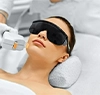
Q Switch Laser Treatment For Pigmentation
Q Switch Laser is a highly effective, safe, and
painless treatment is a popular choice for pigmentation treatment
It addresses major skin concerns with minimal side effects and no downtime required. Laser treatments can target and break down excess pigmentation:
Different Types of Lasers for Melasma Treatment
Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser is a safe and effective treatment for hyperpigmentation, using high-energy pulses to target pigmentation and blood vessels.
Picosecond lasers are effective for dark skin and have a low risk of adverse effects. Fractional resurfacing lasers stimulate the body's natural healing process by creating controlled injuries.
Intense-Pulsed Laser (IPL) targets pigmented cells without damaging the skin, often recommended for treatment-resistant melasma.
The best laser for melasma treatment depends on individual needs and goals. Consult a qualified dermatologist or laser specialist for proper use.
Risks and Protocols
A qualified professional will assess your skin type and recommend the most suitable laser treatment to minimize the risk of thermal injury and hyperpigmentation.
Choose Top Skin & Hair Clinic For Pigmentation Treatment
Hyperpigmentation in brown and black skin requires a customized treatment
plan that takes into account the individual characteristics of darker skin tones.
It can be treated by prioritizing sun protection, using a gentle skin care regimen
and choosing effective treatments. A consultation is necessary to develop a safe and
individualized treatment strategy.
Keva Skin and Hair Clinic offer the
best pigmentation treatment in Coimbatore.